In the late 1920s,. aircraft manufacturers have decided to compare aviation and Navy in the tactics of their operational use. Typically, several cruisers, was included in the squadron, and one or more extended far forward and acted as intelligence. And aircraft manufacturers have decided to design a plane, for tactical combat vehicles suited to the class as "air cruiser". This class was the intermediary between the light twin-engine bomber and fighter. "Air cruiser" was supposed to be a fighter speed and have a radius of action bomber. In addition to the role of bomber defense, on such machines assigned intelligence tasks.
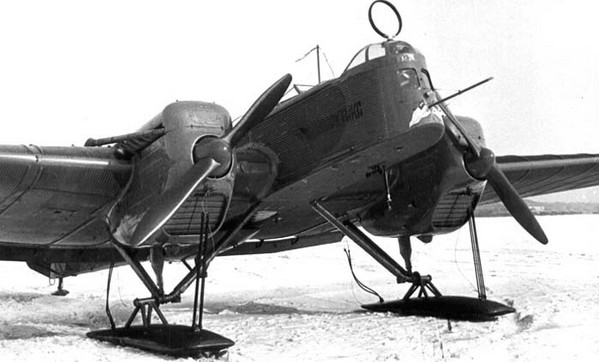
In October 1926 g. on its own initiative, the Design Bureau AN. Tupolev began to design an all-metal twin-engine aircraft P-6 (IPG-7), according to the destination corresponding to the class "air cruiser". ANT-7 is not fundamentally different from the previously constructed TB-1. He inherited from bomber aerodynamic design with cantilever wing monoplane thick profile and had the same engine M-17. Outwardly, little P-6 differed from its predecessor, but it was much smaller in size and weight. So, wing area reduced by half, and the scope of reduced almost 5 m. By August 1927 g. We completed the detailed design and launched the car into production. The main characteristic of his monoplanes-airplanes - specific wing load - AN. Tupolev has kept the same, like the biplanes of those years. This unnecessarily increased machine size, reduced payload, speed and range.
The first prototype was built 26 August 1929 g. In early September, he was transferred to the airfield and began production tests. First Flight F-6 (IPG-7) done 11 September, I drove the car crew test pilot MM. Gromova. According to the results of factory and state tests of the plane in a series of recommended and adopted. The plane was built in several plants and just before production ceased in 1936 g. released 407 ANT-7 all modifications. Further modifications of the basic serial ANT-7, based on them have designed some variants. One of the vehicles was equipped with a closed cockpit and passenger cabin on 7 human. A year later, this plane crashed. One of the mass-produced cars converted into a pilot system to combat air defense barrage balloons under the designation P-6 "otter".

AT 1933 g. appeared marine modification P-6a. Similarly, the TB-1 was equipped with floats and its intended use as a long-range maritime reconnaissance. Float variant "cruiser" P-6a proved less successful, than a similar modification of the TB-1. The floats were too big for him, and its flight characteristics significantly deteriorated. During the test series three cars were smashed. Nevertheless, he was accepted for serial production. After removal planes P-6 with their arms in the transmitted GVF, where they have long been used for freight and passenger transport under the designation PS-7 and MP-6. During the war, they are widely used for reconnaissance, communication, supply of guerrilla bases and compounds regular army.
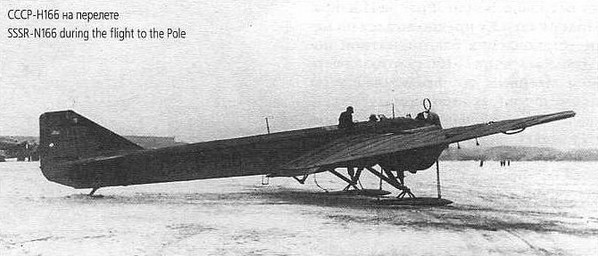
Planes P-6 (IPG-7) actively used in the northern and arctic regions of the country. crew II. Golovin to ANT-7 aircraft ("N-166") participated in the expedition to establish the drifting station NP-1. He wore the same crew 5 May 1937 g. first flew over the North Pole. Aircraft were also involved in the rescue of people from the ships, drifting in the Laptev Sea in the early 1938 g. AT 1939 g. on PS-7 was made ultra-long flight on the route Moscow - Bay length Nagaeva 9222 km.
The plane MP-6 Aviaarktika

modifications
P-6 - modification for reconnaissance and bomber escort, first flight in 1930 year
P-6L ("Limousine") - serial version with a closed cabin in the form of low fuselage add-glazed windows and the entrance door on the right side. 9-seater plane (of them 7 passengers), equipped with storage compartment. It was released in a single copy in July 1933 of the year. I crashed in September 1933 year due to bad weather conditions.
MP-6 "Morskoy sixth scout" - R-6 aircraft on floats of the "F" was produced in 1932-1934 at the factory in Taganrog. Because floats were the same as that of the TB-1, the aircraft was very complex landing. In tests, the aircraft was lost three cars. Used in GVF and NKPS under the trademark MP-6. pilot L. D. Kruse performed on this plane first aerial photography of the taiga, on which later took the route of the Baikal-Amur Mainline. For those years, this was cutting-edge technologies.
KR-17 6-2M "cruiser" - after the discontinuation of the MR-6 Taganrog its production resumed in Moscow under a new name. In addition to the design it was introduced a number of changes - introduced flaps and fairings between the wing and fuselage, removed retractable tower, brake wheels, etc.. "Cruiser" was issued in the years 1934-1935.
PS-7 - civilian aircraft PS-7 (for the carriage of goods and passengers), First there was an open cabin, but later began to make closed. Cockpit pilot and flight engineer were in the front of the aircraft, 8-10 passenger capacity of the passenger compartment. Aircraft flying at a speed of 170-180 km / h.
P-6 - civilian aircraft (for the carriage of goods and passengers).
Passenger P-6 (IPG-7)

The performance characteristics of the aircraft F-6 (IPG-7)
– chief designer: A Tupolev. n.
– First flight: May 1930
– End of operation: 1944
– units produced: 406
Crew P-6 (IPG-7)
– 4 man
Size P-6 (IPG-7)
– Length: 15,06 m
– Wingspan: 23,2 m
– Height: 6,92 m
– wing area: 80 m²
– Wing loading: 76,6 kg / m
Weight P-6 (IPG-7)
– empty weight: 3900 kg
– Curb weight: 4690 kg
– Normal takeoff weight: 6130 kg
Engine P-6 (IPG-7)
– 2 × piston M-17F
– engine power: 2 × 500 HP. (2 × 373 kW)
– thrust-to-weight ratio: 121 W / kg
Speed F-6 (IPG-7)
– Maximum speed at ground: 240 kmh
– Maximum speed at height: 212 km / h on 5000 m
– landing speed: 110 kmh
– set the height: 5000 M 39,3 min
Flight range P-6 (IPG-7)
– 1680 km
Ceiling P-6 (IPG-7)
– 5620 m
Arming P-6 (IPG-7)
– Small-pushechnoe: 5 × 7,62 mm machine guns YES
– combat load: 790 kg
Photo P-6 (IPG-7)












