To fight the enemy ships can use various weapons, but the leading role is currently owned cruise anti-ship missiles. In past, but, discussed and other variants of anti-ship weapon. In particular, considering the introduction of ballistic RCC. In our country, several projects have been developed, none of which, however, I have not reached practical application.
The idea of a ballistic missile, designed to engage large surface ships, formed by the end of the fifties. By the time the likely opponents of our country managed to build numerous and powerful fleets, which ought to fight on distant approaches. Already there were cruise missiles for long-range bombers and submarines, but their flight range did not meet the current requirements. And the aircraft carrier, and the submarine would have been forced to enter the defense area of the ship groups opponent.
The obvious way out of the current situation seen submarine launched ballistic missiles. With its small size and weight, the product of this class could fly to a distance of several thousand kilometers. This makes it possible attack ship connections of the safe area. By the early sixties, it completed the formation of a new concept, that it allowed to move from research to development work.
Projects D-5T and D-5g
The first member of a new program for the development of ballistic submarines RCC became Leningrad CDB-7 (now KB "Arsenal" named. MV. Frunze) headed by PA. Tyurin. FROM 1958 years, the organization has developed a complex of D-6 with a fundamentally new solid-fuel rocket. Consideration revealed, such that the missile can be taken as basis for the perspective of RCC with sufficiently high performance. As a result of this project I started with the working designation D-5T.
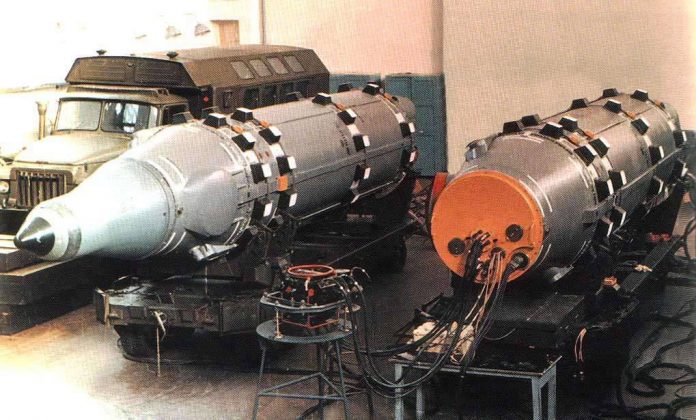
 Layout missile complex D-6 on parade.
Layout missile complex D-6 on parade.
Basic missile complex D-6 was a two-step product with solid engines. At each step proposed to use four separate engine in separate housings. Besides, on the fairing envisaged starting engines, intended to exit the launcher. Elaboration of a new project showed, that the missile complex D-5T will be able to fly at a distance of up to 1500-2000 km. Increasing the range in comparison with the reference sample was achieved by reducing the weight of the head portion.
At the beginning 1961 year to work on new topics Miass joined SKB-385 (now they SRC. VP. Makeyev). his project, get a working designation D-5g, It involved the creation of an entirely new missile with liquid propulsion. Such a rocket would send a special warhead at a range of 1800 km.
Carriers of the D-6 were to be diesel-electric and nuclear submarines of several projects. As the carrier system D-5T considered only specialized modification project 661. The issue of creating a submarine was worked in the CDB-16 (now SPMBM "Malachite"). Later, after the onset of the project D-5g, there was a proposal for the adaptation of the two complexes for use on submarines modified project 667. However, to develop such a project would take time, which led to the unusual offer. SKB-385 was assigned to work out variant ballistic RCC for based on special surface ships.
Further development of the two projects has led to the abandonment of a solid-fuel rocket. It was found, that the complex D-5g will be more convenient to use, and because this is the project to be developed. Further development of the new project was conducted under the designation D-5. Finally, It was taken another important decision. submarines promising weapon was supposed to be a rocket of a new modification, originally worked out in the framework of the ship's weapons.
Complex D-5 with a missile F-27K
In April 1962 the USSR Council of Ministers decided to begin development of a new anti-ship missile system for submarines. The complex generally designated as D-5, rocket for him - P-27K or 4K18. As follows from the designation, new RCC was supposed to be a special modification of the average R-27 type range of the existing missiles.
In just a few months, SKB-385 formed the shape of the new complex and determined the range of necessary improvements of the existing missiles. It proposed to use a two-stage rocket, wherein the first stage of the second charge of the output to a predetermined trajectory. The second stage, respectively, I had to carry tools and homing warhead. Since it was the defeat of moving targets, rocket was bound to carry a means of detecting and homing.
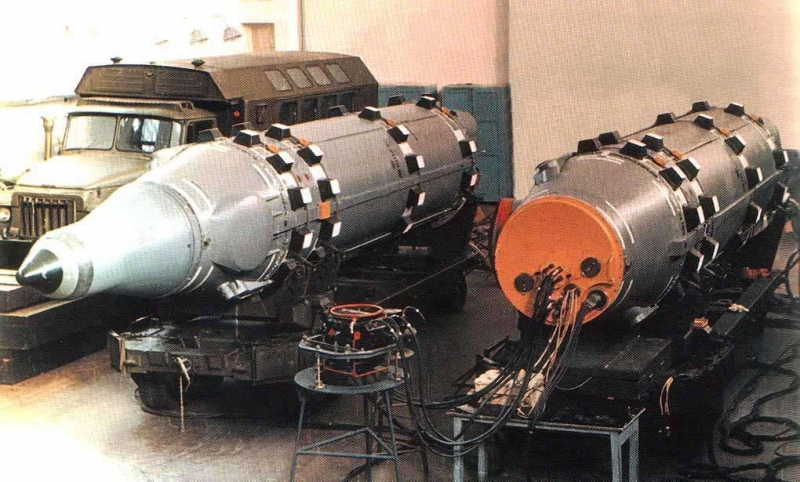 Rocket R-27K (left) and the P-base 27 during testing.
Rocket R-27K (left) and the P-base 27 during testing.
In the same time, it was found, that RCC development faces a number of difficulties. So, and guidance control means with the desired characteristics were too large. Because of this, the second stage can take up to 40% from the allowable size of the product. Besides, seeker had to close the radio waves heat resistant radome. Suitable materials at that time in our country there were no.
The difficulties have led to the emergence of two preliminary drafts. They used a common first step, based on units of R-27 missiles, and the second stage designed from scratch. The first step differs from the base structure body with a shortened reduced capacity tanks. engine 4D10, control means, etc.. remained the same. Two versions of the second stage, differing equipment and operating principles, We were designated "A" and "B".
Both projects are offered the use of passive radar homing head with the antenna side-view. Until a predetermined time the antenna is folded should be within the housing, and then go outside and lay. In this case, you can search for signals from the electronic systems of the enemy ship, which could determine its location and adjust the missile course.
The "A" offers a relatively complex control system. At the upstream portion of the missile trajectory was corrected trajectory by means of special motors second stage. At movement downwards, to the goal, should use the aerodynamic control surfaces and adjust the course according to the head of the antenna, receiving signals from the front hemisphere. In the project "B" course correction was proposed to use just before entering the descending part of the trajectory. The first version of the guidance means has been much more difficult, and increased overall dimensions of the second stage, but it could give greater accuracy of hitting the target.
For further development has been adopted version of the second stage with the letter "B". In this way, 4K18 rocket / P-27K had to seek the goal with the help of passive homing with the antenna side-view. The need for the antenna head has disappeared. For further development of electronics in the project attracted the NII-592 (now NPO Automation). With it, an improved GOS to more efficient antenna has been established.
The product F-27K, project, It had a length 9 m at a diameter 1,5 m. Starting weight - 13,25 t. From the base R-27 externally it differed extended payload fairing more complex shape. The second stage was carrying a special warhead capacity 650 CT, able to compensate for a decrease in accuracy. Rejection of full power setting in the second stage and decrease supply of fuel in the first led to a reduction flight range. So, P-base missile flew to 27 2500 km, whereas the new 4K18 - only 900 km.
It should be noted, that work on the project P-27 and P-27K have been associated with certain difficulties. Consequently, the base ballistic missile entered service only 1968 year, and testing of RCC was able to start in just two years. The first test launch 4K18 / P-27K was performed at Kapustin Yar in December 1970 of the year.
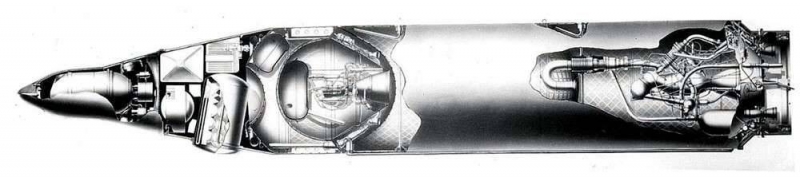 The circuit of the second stage rocket 4K18 type "B".
The circuit of the second stage rocket 4K18 type "B".
Using ground launcher performed 20 test runs, of which only 4 were alert. Further held several throwing starts with sinking stand. After that, work began on preparing the missile system testing on the submarine carrier.
It should be noted, that since the mid-sixties design D-5 encountered certain difficulties in terms of media search. Some of the submarine did not meet technical requirements, while others can not be used with RCC, as it should have been borne by strategic missiles. As a result, an experienced carrier complex decided to make diesel-electric boat K-102 project 629. In accordance with the new project "605" it was to receive four launch tubes and a set of different equipment to work with missiles.
9 December 1972 , the submarine K-102 for the first time launched a missile R-27K. The tests continued for about a year, and during that time used 11 advanced missiles. 3 November 1973, was held on doubles by missile launch barge target. One product 4K18 when it hit right on target, and the latter committed a minor mistake. Important, that at the time of launching missiles reached the target position uncertainty 75 km. Despite this, missiles found yourself a target, and brought her.
Despite the successful completion of tests, in early September 1975 the project D-5 / P-27K closed. Passive radar homing could not provide the required reliability problem solving, and the opposition to it is not difficult. Nuclear warhead, in its turn, It hampered the deployment of submarines with the new PKR due to the presence of new international agreements. Finally, there has been significant progress in the field of cruise missiles. In this situation, the available range of D-5 is not of interest to the Navy.
Complex D-13 P-33 rocket
Shortly after the start of the missile tests P-27K, In the middle 1971 of the year, SKB-385 received a new assignment. Now it was required to create a range of D-13 with anti-ballistic missile R 33. The latter was based on the R-29 product design and hitting targets at ranges of up to 2000 km by means of one-piece or split warhead.
The development of the R-33 missile was carried out using the basic ideas and concepts of the previous project P-27K. So, P-29 base planned "shortened" to two stages, but to collect from ready-made components. First stage, as earlier, He was responsible for the acceleration of a rocket, and the second was proposed to mount a warhead and guidance means. Due to the special apparatus the second stage was obtained a sufficiently large and heavy. Despite this, rocket as a whole had to comply with the limits of existing launchers.
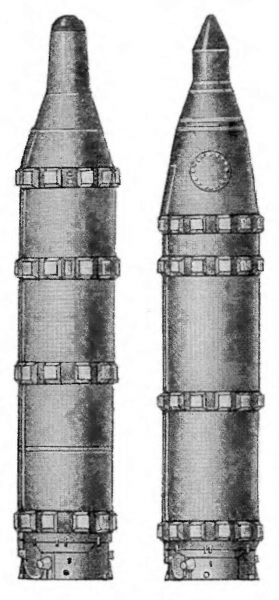 Comparison of R-27 and F-27K (left).
Comparison of R-27 and F-27K (left).
To increase the range of fire, coupled with the increase in target detection distance, demanded better seeker. It is large in size, and this led to a reduction in the size of the first stage to the second. Reduction of tanks first step could lead to a reduction in the flight range of up to 1200 km. Also, there were serious problems with the conditions of the systems. Seeker of a new type needed radome, capable of withstanding the high temperatures during the descent. In this case, could be generated plasma cloud, least, obstructing the work of electronic systems.
Yet in 1974 by SKB-385 was able to solve some of the problems and to provide preliminary design missile complex D-13. The first stage of the rocket, unified with the product P-29, It equipped with tanks for UDMH and nitrogen tetroxide, as well as carrying 4D75 engine. The second stage did not have a full power plant and equipped only for maneuvering engines. It also arranged passive radar seeker with a pair of antennas, controls and special warhead. By improving systems, accompanied by a decrease in their size, It managed to increase fuel capacity and range up to bring 1800 km.
according to the preliminary design, R-33 had a length of 13 m at a diameter 1,8 m. The starting weight during the design repeatedly varied from 26 to 35 t. As a carrier of such rockets throughout the development were considered boats 667B project. To use the new anti-ship missiles such as they were to receive the equipment receiving target designation and management of a rocket during prelaunch.
According to the plans of the seventies, Soon the project were to consider the specialists of the military department. Start testing planned for the end of the seventies, and by the middle of next decade, the complex D-13 could go into service.
However, this did not happen. Customer analyzed the existing project and decided to give it up. In early September 1975 the order of one year were halted two projects - D-5 / F-27K and D-13 / P-33. The reasons for refusal of the two complexes were similar. They did not show the desired specifications, actual combat effectiveness is limited by the characteristic problems of guidance means, and the presence of a nuclear warhead to impose restrictions on the deployment of.
RCC-based ICBMs
As is known, intercontinental ballistic missile UR-100 was originally seen as a means to solve a variety of combat missions in different terms,. among other things,, I worked through modification of such missiles to be placed on submarines. According to some reports, examined the possibility of using modified SD-100 as anti-ship weapons.
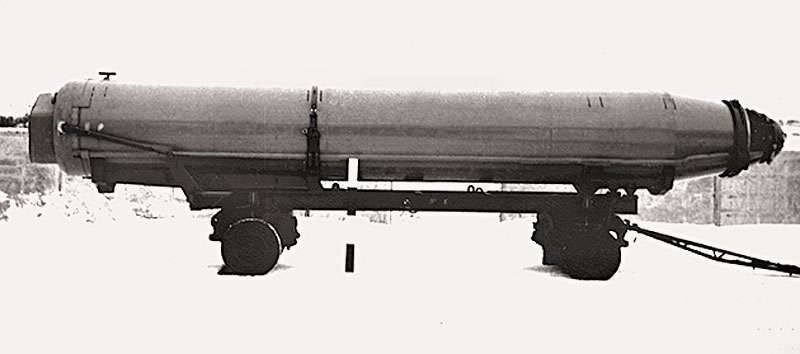 Missile P-29, on the basis of which the product was produced by P-33.
Missile P-29, on the basis of which the product was produced by P-33.
According to reports, that at a certain time in the OKB-52 under the direction of VN. Chelomeya elaborate on existing ICBMs under the special challenges. By substantial processing design the product SD-100 could be the anti-ship missile, are of the highest firing range and special power warhead. However, as far as, This project, along with several others remained at the preliminary study stage. A full project is not developed, RCC and experienced-based UR-100 were not tested.
However, we know, in the middle 1970 It was held two UR-100 launch experimental rockets, equipped with radar homing. maybe, These tests have been directly related to the study of the creation of advanced anti-ship missile medium-range intercontinental.
Some sources mention the idea of creating anti-ship missile on the basis of "land" ICBM complex "Topol". However, in this case, the idea has not been implemented. Furthermore, there is every reason to believe, that such a project or proposal has never existed and in fact we are talking only about the rumors.
***
At the end of the fifties the Soviet Union faced some challenges in the fight against a potential enemy naval group. existing weapons, is able to sink big ships, It had limited features and forced divers and sailors risk. In such circumstances, a promising tool in the fight with the enemy could be a promising ballistic anti-ship missiles.
For several years, Soviet industry has developed a number of such projects. Two projects antiship RCC reached the stage of full development work, and one of them even brought to the test. During the project D-5 and D-13, interesting results have been obtained, but their practical perspectives have been mixed. The presence of a number of technical difficulties and limited combat capabilities are not allowed to fully realize the full potential of new weapons.
Besides, in the course of the work has affected the success in other areas. By the time of completion of the rocket design P-27K, new samples of aviation equipment, as well as cruise missiles for aircraft, ships and submarines. Modern weapons of this kind in a number of ways superior ballistic RCC and make them irrelevant. As a result of such weapons in our country refused. After 1975 of the year, when the military decided to close the project D-5 and D-13, new systems of this kind have not been developed.
Based on materials:
— makeyev.ru
— alternathistory.com
— rbase.new-factoria.ru
— nvo.ng.ru
— deepstorm.ru
— otvaga2004.ru
— defence.ru
— bastion-karpenko.ru
- Shyrokorad AB. Weapons domestic fleet. 1945-2000. Minsk: harvest, 2001.











