Medium tank T-62, unlike its older counterparts - tanks T-34, T-43, T-44, T-54, created under the leadership of A.A.. Morozova, designed under the leadership of L.N.. Karceva, who took the post of chief of the design bureau of the Uralvagonzavod (UVR) in Nizhny Tagil, after A.A.. Morozov to Kharkov.
According to rough estimates, over the years of production, more than 20 thousand. these machines. And although it is significantly less than those 80 thousand. copies, in which his progenitor was multiplied - T-54/55, but even such a figure inspires respect. As the, that the T-62 was or is in service with more than two dozen different states.
 Medium tank T-54 — predecessor of the T-62
Medium tank T-54 — predecessor of the T-62
History of creation
The background to the creation of the T-62 dates back to the dawn of the 50s, when the Scientific and Technical Committee of the Main Armored Directorate of the Soviet Army (NTK GBTU) formulated tactical and technical requirements (TTT) to a promising medium tank of the second post-war generation. In accordance with them, a promising medium tank should have significantly surpassed in basic indicators (firepower, security and mobility) the first Soviet post-war medium tank - T- 54, which during this period was just beginning to enter service with the Soviet Army in significant quantities (CA).
Despite, that T- 54 was at that time the world's best medium tank, its design was based on the experience of the use and operation of armored vehicles during the Second World War. However, over the past post-war years, new types of weapons have appeared., which significantly changed the nature of hostilities.
At first, the United States has accumulated a significant arsenal of nuclear weapons, including tactical purposes, the USSR had the same weapon. As a result,, the use of nuclear weapons in a possible conflict has become highly probable. Besides, at the same time, in many Western armies, a new, a very effective means of fighting tanks - anti-tank guided missiles (PTUR) with cumulative warheads, which significantly increased their armor penetration.
All this, as well as the further development of armored vehicles in the countries of a potential enemy made it necessary to carry out development work to create a new promising Soviet medium tank. The situation was further complicated by the fact, that although the beginning of work on the T-54 refers to 1944 city, but the development of its design was delayed, and the tank acquired its final form only by the beginning of the 50s. At the same time, its truly mass production began.. To 1951 g. only about 3,5 thousand. T-54 (sample 1946 and 1949 gg.).
If we add to this 1,8 thousand. T-44, production of which ceased already in 1947 city, the, without risking mistakes, it can be argued, that the most massive medium tank SA in the early 50s were still "thirty-fours", obsolete by that time not only morally, but physical.
design offices
During the period under review, four design bureaus were engaged in the development of tanks in the USSR.. Design bureaus of Leningradsky Kirovsky (LCO) and Chelyabinsk Tractor Plants (ÇTZ) designed heavy tanks. The middle ones were traditionally dealt with by OKB-520 of plant # 183 (starting with the first "thirty-fours"), from which, by the beginning of the 50s, two tank design bureaus were actually formed - design bureau of plant No. 183 or Uralvagonzavod (UVR) in Nizhny Tagil and KB-60 at the plant number 75 in Kharkov.
The history of this division is as follows: at 1941 g. OKB-520 was evacuated from Kharkov together with plant No. 183 to Nizhny Tagil to the territory of UVZ, and it was here that this team, led by A.. Morozov, medium tanks T-44 and T-54 were created. However, by the end of the 40s. most of the experienced tank designers evacuated to Nizhny Tagil returned to Kharkov to the newly organized plant No. 75.
And 1951 year, the post of chief designer of the tank KB-60 of this plant was taken by A.A. Morozov, who returned from Siberia (according to one of the versions, his departure from factory # 183 was due to disagreements with the management, just on the fundamental issues of the design of the new tank). The design bureau team remaining in Nizhny Tagil, mostly youth, headed by designer L.N.. Karcev.
Considering, that the bureau of Uralvagonzavod has not yet received sufficient experience after the departure of the Kharkov designers, as well as the high authority of A.A.. Morozov as the creator of a number of successful designs, work on the creation of a new promising medium tank was originally entrusted to KB-60 of the Kharkov plant number 75.
"Object 430"
Work on a promising tank began in 1951 city, and to 1953 g. a pre-sketch project has already been developed in Kharkov, which surpassed the serial T-54 in all main parameters. The car received the designation - "object 430". by the way, the first number in the designation of post-war Soviet armored vehicles almost always determines the design bureau of the vehicle's developer. Например, numeral 4 means, that the machine was developed by KB-60 at the Kharkov plant No. 75, numeral 1 Is a technique, designed in OKB-520 of plant # 183 (or UVZ) in Nizhny Tagil.
According to the project "Object 430" armed with a 100-mm tank gun D-54TS, for which, for the first time, an optical sight-rangefinder TPDMS was installed on a medium tank. Its armor protection was strengthened by slightly increasing the thickness of the armor parts and installing them at large angles of inclination..
 A prototype medium tank "Object 430" with a 100-mm D-54TS tank gun
A prototype medium tank "Object 430" with a 100-mm D-54TS tank gun
The prototype "object 430" had a welded hull, made of rolled armor plates. Its nose was a multi-layer armor barrier with a rational angle of inclination of the front and zygomatic sheets. A spherical turret with a narrow embrasure for mounting a gun had a differentiated three-layer armor protection..
Cannon D-54TS, coaxial with 7.62 mm PKT machine gun, stabilized in two planes by the stabilizer of the tank armament "Blizzard" and had a mechanism for ejection of spent cartridges. The tank was equipped with an optical rangefinder sight TPD-43 (TPDMS) with independent stabilization of the field of view in the vertical plane. To combat low-flying enemy targets, it was planned to install an anti-aircraft machine gun on the tank, equipped with a 14.5 mm KPVT machine gun.
The tank was equipped with a more powerful 5TD five-cylinder engine. (580 hp). Transmission - mechanical planetary. "Object 430" had a new undercarriage with small diameter road wheels with internal shock absorption (instead of the large rollers used since the BT and T-34 tanks) and track with metal hinge. Tank suspension system - individual, torsion bar with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers on the first and sixth suspension nodes.
The tank was equipped with a system of collective protection against weapons of mass destruction and an automatic PPO system. AT 1957 g. three prototypes of the Kharkov "object 430" were ready.
Tests of "object 430" were generally successful, although they revealed a number of shortcomings. In the conclusion of the test commission it was written, that the requirements of the task Scientifically- of the GBTU technical committee were generally fulfilled, and the experienced tank outperforms serial medium tanks in its characteristics. But to achieve a significant increase in its firepower compared to the T- 54 the designers failed, and given the fact, that its design was completely new, during its serial production, inevitable problems would arise when organizing service, personnel retraining and repair. Therefore, the adoption of the "object 430" was considered inappropriate. Its designer, A.A.. Morozov.
Object 140
AT 1952 g. Nizhny Tagil Design Bureau also joined the work on a promising medium tank. His new boss L.N. Kartsev, despite the existing staffing problems, managed to obtain a government assignment to develop a promising tank.
Very large, if not the main, the role in this was played by the director of UVZ I.V.. Okunev is a man of irrepressible character, strong-willed, highly respected in the Ministry of Transport Engineering. He showed a constant interest in new technology and was a patriot of his plant.. And getting such a serious government assignment for KB, and promised great advantages for the plant: increased funding, influx of qualified personnel, gaining experience, and most importantly - the deployment in the future of serial production of a new tank.
Nizhniy Tagil project received the designation "object 140". The future vehicle was supposed to have a new armored hull., improved form, arm with a D-54T gun (as well as "object 430"), a new diesel D-36 was supposed to be the engine (the maximum power of which, according to some sources, should have been 700 hp).
Experienced "Object 140" had a body with large angles of inclination of armor plates (including sides and roofs). Armor thickness of the forehead of the case - 100 mm. Tower, in shape strongly resembling the T-54 tower, had a booking in front of before 240 mm. The armament was similar to the "object 430". The gun was guided using the TSh-2 telescopic sight.
Engine - V-36 multi-fuel diesel, power 700 HP, which was a modification of the B-2 family engine. Transmission - mechanical planetary. Undercarriage - with small track rollers, with external depreciation, and supporting rollers. AT 1957 g. a prototype of the Nizhne-Tagil "object 140" was built.
Tests of "object 140" revealed a number of serious flaws in the design of the engine and transmission, Besides, despite a large number of progressive design solutions, in general, the car turned out to be very low-tech. In the end, The chief designer of the UVZ design bureau L.N. Kartsev sent a letter to the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers with a request to release his design bureau from continuing work on the project of a promising medium tank.
Both prototypes, after passing factory tests, took part in comparative tests at the Scientific Research Institute BT Polygon in Kubinka.
Implement development
U-8TS. At the same time, as part of the creation of a promising medium tank to increase its firepower in OKB-9 under the leadership of F.F.. Petrov, work began on the development of a 100-mm rifled tank gun with a more powerful, than the D-10T installed on the fifty-four. The initial velocity of the armor-piercing projectile of the new gun was supposed to reach 1015 m / s (Compare, to D-10T - 895 m / s), and the muzzle energy be on 30% higher.
To compensate for the increased recoil, a muzzle brake was installed., an ejector was used to purge the bore. Cannon, received the designation D-54T, it was planned to install in the T-54 tank instead of the D-10T, it was also supposed to be used to arm a promising medium tank..
 Prototype medium tank "object 140". This vehicle is also armed with a 100 mm D-54TS cannon.
Prototype medium tank "object 140". This vehicle is also armed with a 100 mm D-54TS cannon.
To test this weapon in 1954 g. in Nizhny Tagil, an experimental tank was built on the basis of the T-54 hull and turret, received the designation T-54M or "object 139". Only in June 1954 g. in TsNII-173 the technical project of the single-plane stabilizer "Raduga" was completed. And the first prototype D-54 was installed on "object 139" in October 1954 g. At the same time, "Object 139" was accepted by the commission and sent to the factory field tests, the first stage of which was completed by December 1954 g.
There were also firing from a new gun, however only from the spot, since TsNII-173 delayed the delivery of the Raduga stabilizer. The tests continued in 1955 g. after installing the stabilizer, but his work was unsatisfactory, Besides, It revealed, that the maintenance of the gun is difficult due to the tightness of the fighting compartment - the D-54 was large, than D-10T. The stabilizer "Rainbow" was not adopted for service, further work on the T-54M also stopped, since about the same time, the T-54A tank entered service, equipped with a single-plane stabilizer "Horizon".
After the failure with the "Rainbow" for the D-54 cannon, the TsNII-173 designed a two-plane stabilizer "Molniya". In the autumn 1955 g. UVZ received three prototypes of the stabilized in two planes 100-mm D-54TS cannon with "Lightning", intended for "object 140".
AT 1958 g. testing of new guns was started on three prototypes of "Object 165" (a story about him below). By February 1960 g. field trials of "Object 165" have been completed. The D-54TS cannon withstood them., which by this time was somewhat modernized - the barrel was strengthened, as a result of which his weight increased to 2390 kg, the steepness of the rifling has been changed in connection with the beginning of the development of a new subcaliber projectile. This version of the D-54TS gun received the factory index U-8TS and the GRAU 2A24 index. AT 1961 g. "Object 165" with 100-mm cannon U-8TS with stabilizer "Meteor" was put into service under the designation T-62A. Its ammunition included only caliber armor-piercing and fragmentation- high-explosive shells, since the development of subcaliber armor-piercing projectiles was delayed.
U-5TS. Late 50s, in the USSR, a 100-mm smooth-bore anti-tank gun T-12 "Rapier" was developed with very high armor penetration characteristics for that time. At the same time, the idea arose to install "Rapier" in the projected "Object 165". However, the Rapier's unitary shot was too large, its length was 1200 mm, and in the tower of "object 165" he did not get mad. Then it was decided on the basis of the 100-mm rifled gun D-54 to design a smooth-bore tank gun with the same, like D-54, shot length (1100 mm).
The use of a smooth barrel promised a number of advantages, among which there was an increase in pressure in its channel in 1,5 — 2 times compared to the D-25TS and the elimination of the negative effect of projectile rotation on the formation of a cumulative jet (ie. relative ease of creating a powerful cumulative projectile).
The new gun was developed at OKB-9 under the leadership of F.F.. Petrova. During the work it turned out, what, eliminating rifling and without changing any external dimensions of the D-54, you can increase the caliber of the gun with 100 to 115 mm. They decided to abandon the muzzle brake, the ejector was moved closer to the middle of the barrel. The rest of the gun elements were completely borrowed from the D-54.. The result was the world's first smooth-bore tank gun U- 5Vehicle with an initial projectile velocity of 1620 m / s ! . Its ammunition included unitary shots with armor-piercing- subcaliber, cumulative and high-explosive projectiles.
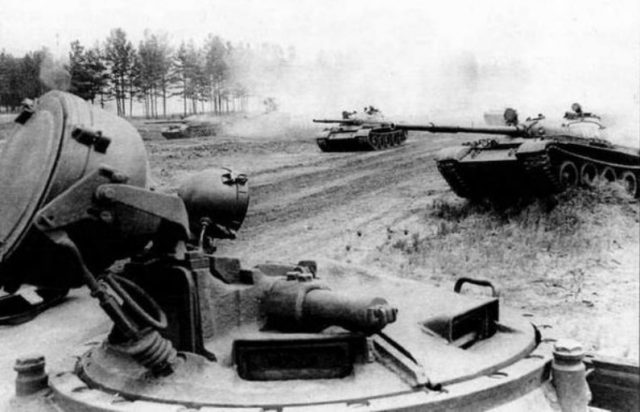 Medium tank T-62 in service with the Soviet Army
Medium tank T-62 in service with the Soviet Army
Object 165
In this way, despite the long efforts of two competing tank design bureaus, to 1957 g. The Soviet Army never received a new medium tank, which would significantly exceed the T-54 already available in the troops. The situation escalated even more after military intelligence received information about the development in England of a new extremely powerful 105-mm rifled tank gun L7A1.
Due to the very long barrel (62 калибра) and high pressure in its channel (5500 kg / cm) the armor-piercing sabot projectile of this gun had an initial velocity 1470 m / s and significantly exceeded the shells of the Soviet D-10T cannon in terms of armor penetration.
AT 1958-1959 gg. British heavy tanks "Centurion" of modifications Mk IX and Mk X with these guns were expected to enter service, in the future, it was also supposed to be installed during the modernization and on the previously released "Centurions" modifications Mk V and Mk IV. Besides, to 1960 g. mass production of the new American medium tank M60 with the same 105-mm cannon was to begin, manufactured under license in the USA under the brand name - М68. Given this disturbing information, GBTU demanded that the designers immediately increase the firepower of Soviet medium tanks..
As a result, the UVZ design bureau urgently resumed work on strengthening the T-54 armament, why it was supposed to use the D-54TS cannon with a mechanism for ejection of spent cartridges. The project of the tank received the designation "Object 165". In order to reduce technical risk and the fastest possible launch of the tank into production, T-54/55 units and assemblies were used for it..
Однако, given experience, accumulated during tests of "object 137" and "object 140", and that, that the new 100 mm cannon had a slightly larger breech and a longer shot, than D-10T, and GBTU forbade the introduction of separate-case loading, the designers had to design for the D-54TS installation a new one-piece tower with an increased ring diameter - 2245 mm instead 1825 mm in T-54. At the same time, the thickness of its booking was increased - up to 240 mm in front.
To facilitate the work of the loader, and also to solve the problem of removing large spent cartridges, which was already irrational, like before, put back on shelves, on the cannon fence (as on the "object 140" developed earlier in this design bureau) installed a mechanism for ejection of spent cartridges. The casings were thrown out through a small hatch in the rear of the tower.. The new big tower could no longer fit on the old building, so it was necessary to lengthen its front part and move the engine compartment back.
As a result, a new body was designed - longer and somewhat wider. The thickness of its frontal sheets has not changed, remaining equal 100 mm, but in other directions, the thickness of the armor had to be somewhat reduced with its strong differentiation, to facilitate the tank. This was necessary to keep his mobility at the same level., since the power of the power plant has not changed - the engine-transmission compartment with all units remains the same, as on the T-55.
The undercarriage also remained practically unchanged - the support rollers, drive and guide wheels (only the number of tracks in the track has increased - 97 instead 90 at T-54, by lengthening the body), but to maintain the correct centering of the tank, the location of the road wheels was changed (unlike the T-54, which had a large gap between the first and second rollers, rollers on the T-62 were concentrated in the front, the most difficult, body parts). As a result of a chain of such changes, caused by the use of a more powerful cannon, and there was "object 165" - the future T-62A.
Relatively new system, which was installed on "object 165", was the anti-nuclear protection system (GROOVE), which was designed to protect the crew and equipment inside the tank from the impact of the shock wave of atomic ammunition, as well as to protect the crew from exposure to radioactive dust in radioactively contaminated areas. A similar system just at this time was installed in the UVZ design bureau on a modernized version of the "fifty-four", serially named T-55. Looking ahead, can say, that the T-62 became the second serially produced Soviet tank (after the T-55), having a PAZ system.
AT 1958 g. three prototypes of "Object 165" with 100 mm D-54TS cannons were made. Their tests took place fairly quickly and without any particular complications., tk. almost all components and assemblies were already tested on the ‘G-54/55 and were mass-produced.
Object 166
At the end 1959 - early 1960 G. G. 115- mm gun U-5TS was installed in the converted "object 165". This experimental vehicle received the index "object 166". AT 1960-61 gg. "Object 166" successfully passed factory and military tests and in August 1961 g. was put into service under the designation T-62. true, during the tests revealed, that despite the increased volume of the fighting compartment, loading the U-5TS cannon with unitary shots is a rather laborious process, especially on the move tank, even despite the presence of a mechanism for ejection of spent cartridges.
In this way, in KB UVZ under the leadership of L.N. Kartsev in a very short time (in three years) two variants of a medium tank with a more powerful, than the T-54, armament and enhanced armor - T- 62A ("Object 165") with 100 mm rifled cannon U-8TS and T-62 ("Object 166") with smooth-bore 115-mm gun U-5TS.
Both tanks in the middle 1961 g. were adopted by the Soviet Army. This made it possible to somewhat smooth out the alarming situation., that arose after the failure of the competition for the design of a promising medium tank and the expected appearance of new British and American tanks.

AT 1961 g. plant number 183 produced an initial batch of T-62 tanks from 25 pcs, which were sent to the troops of the Carpathian Military District. In March 1962 g. the management made a decision "in connection with the need to reduce the range of tank guns, the production of the T-62A should not start". A certain role in this decision was played by the absence of a subcaliber armor-piercing projectile for the U-8TS cannon..
Also, her muzzle brake caused a lot of criticism.. In winter, when firing, the muzzle brake raised a snow cloud, in summer - dusty or sandy. This unmasked the tank and "blinded" its observation devices. The muzzle wave negatively affected the landing on armor and infantry, advancing along with tanks. A significant disadvantage of the muzzle brake was the decrease in accuracy.. As a result, 1 July 1962 g. factory # 183 started mass production of only T-62 tanks with 115-mm smoothbore gun U-5TS.
The main advantage of the T-62 was its almost complete unification with the serially produced T-54 and T-55 tanks., which facilitated the supply of spare parts, simplified crew training, a, Consequently, and the development of a new tank in the army.
The T-62 tank was first demonstrated to the general public four years after it was put into service - at a military parade in Moscow 1 May 1965 g.
Medium tank T-62
Design
The T-62 tank is a further development of the T-54/55 and is made according to the same design scheme., as his predecessor. On the left in front of the hull is the control compartment, the fighting compartment is located in the middle under the turret, and in the stern - power. It uses the same components and assemblies, as in the T-54/55, however the hull and turret are redesigned.
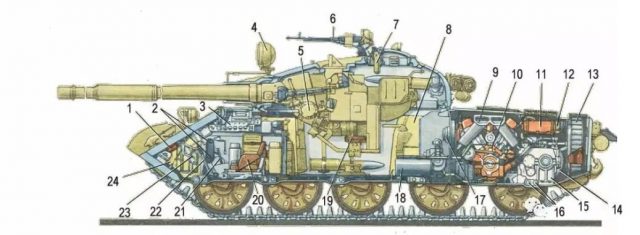 The layout of the T-62 tank:
The layout of the T-62 tank:
1-booster of the hydraulic friction drive of the main friction; 2 — rechargeable batteries; 3-control compartment switchboard; 4 — sight spotlight; 5-gun lifting mechanism; 6-anti-aircraft machine gun; 7 — night-vision device; 8-medium fuel tank; 9-ejector; 10-engine; 11-engine lubrication radiator; 12-engine cooling radiator; 13-fan; 14-planetary rotation mechanism; 15 — Transmission; 16-torsion bars; 17-crew compartment fan; 18-nozzle heater; 19-gunner's seat; 20-driver's seat; 21-gear lever; 22- left control lever PMP; 23-main clutch release pedal; 24-front fuel tank.
The T-62 hull is welded from homogeneous armor plates. Compared to the T-55, the hull length is increased by 386 mm, height on 27 mm. The front plates are thick 102 mm and a significant angle of inclination from the vertical: top - 60 °, bottom - 54 °. The thickness of the rest of the armor is significantly less - the sides in the lower part of the hull - 15 mm, at the top - 79 mm (side plates are installed vertically), the bottom is made of armor steel thick 20 mm and had a trough-like shape to increase strength, roof - thick 31 mm.
There is a mechanic's seat in the control compartment located in the front of the hull at the left side- driver. To the right of it are the racks, in which part of the ammunition rack is located (16 shots) and rechargeable batteries. The driver gets inside the car through his hatch, arranged in a turret leaf above his seat.
In the "combat" position (with closed hatch) the mechanic's view of the area is provided by two periscopes, mounted in front of the hatch. At night, the left periscope changes to a TVN-2 night vision device. It provides a view in a sector of 30 ° at a distance 60 m. Infrared (IK) driver's spotlight is installed on the right side of the upper windshield plate. The control department has a gyroscopic heading indicator GPK-59. The escape hatch is located in the bottom behind the driver's seat and opens inside the tank.
A circular rotation tower is installed in the central part of the building. Unlike the T-54/55 tanks, in which the tower was made cast with a welded roof, the T-62 tower was one-piece. It is slightly larger in size than the T-55 tower - the diameter of the tower support was increased from 1825 mm 2245 mm and has very thick walls: 240 mm in front of and 153 mm on the sides.
The gunner's seats are located on the left side of the tower. (ahead) and the tank commander (behind and slightly higher). On the right side is the loader's workplace. In the roof on either side of the cannon there are hatches that open outward.
The T-62 was equipped with complex screen protection ZET-1, which consisted of mesh and side screens, designed in 1964 year to improve the protection of Soviet tanks from cumulative ammunition, armor penetration of which had significantly increased by this time.
Equipment
To observe the terrain, the commander has a TKN-3 combined day-night device with an IR illuminator, installed in front of its hatch. The range of the IR illuminator is 400 m. In addition to TKN-3, the commander has four periscopes, two of which are installed in the manhole cover, and the other two are in front of the hatch.
The whole complex of observation devices is mounted in the commander's cupola, which has the ability to rotate regardless of the rotation of the tank turret. Telescopic sight TSh2B-41 is installed at the gunner's workplace. At night, the gunner monitors the terrain using an active night vision device TPN1-41-11. IK- illumination by a spotlight, mounted in front of the turret next to the cannon. The viewing range is 800 m.
Besides, the gunner has one prism observation device. The loader's workplace is equipped with one MK-4 periscope, which is installed in front of its hatch. FROM 1975 g. on the T-62 began to install (over the barrel of the gun) laser rangefinder KTD-1 or KTD-2.
To provide external communication, the T-62 was equipped with the R-113 radio station. Communication between the crew members was provided by the R-124 tank intercom.
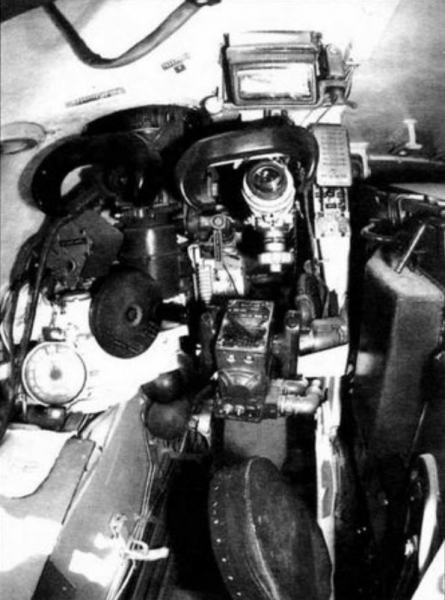 Gunner's workplace. Noteworthy is the location of the scopes. Case — Telescopic TSH2B-41, left — periscopic night sight TPN-1
Gunner's workplace. Noteworthy is the location of the scopes. Case — Telescopic TSH2B-41, left — periscopic night sight TPN-1
Tank T-62 is equipped with an automatic fire extinguishing system. Protection system against weapons of mass destruction, installed on T-62, similar to this system on the T-55. The T-62 is equipped with thermal smoke equipment, standard for Soviet tanks., providing the setting of a smoke screen up to 400 m, which, in calm weather, lasts for four minutes.
The tank is structurally adapted to overcome water obstacles. As mentioned, fords up to 1,40 m T-62 overcomes without preparation. After preparation, using OPVT, the tank is able to overcome water obstacles up to 5 m.
Some of the T-62 tanks were adapted for the installation of various additional attachments.. This is how mine trawls KMT-4 and KMT-5 were used., tank bulldozer BTU, complex screen protection ZET-1.
weaponry
For the first time in the history of world tank building, a 115-mm 2A20 smoothbore gun, stabilized in two planes, is installed in the turret as the main armament (military designation U5-TS "Hammer"). She can fire unitary shots with three main types of feathered projectiles: high-explosive HE- 18, cumulative BK-4 and BK-4M and armor-piercing sub-caliber BM-6.
The APCR shell has a very high muzzle velocity (1615 m / s). Its armor penetration at range 2000 m is 270 mm on vertically arranged armor and 115 mm on armor with an angle of inclination 60 degrees, - this is higher, than similar shells of the 105 mm British L7 cannon. Direct fire firing range is 4000 m, greatest firing range - 5800 m.
Due to the presence of the two-plane weapon stabilizer "Meteor", aimed firing from the cannon can be carried out while the tank is in motion (at speeds up to 10-15 km / h).
Ammunition T-62 consists of 40 unitary shots, which are quite heavy, громоздкими, which requires a lot of time and effort when reloading the gun. Because of this, the rate of fire of the T-62 cannon is very low - when firing from a standstill it is 4-5 shots per minute, which is a serious drawback of the T-62. for comparison: the rate of fire of the T-54/55 cannon is 7 rounds per minute.
The cannon is paired with a PKT machine gun caliber 7,62 mm with ammunition in 2000 rounds.
Initially, the T-62 was produced without anti-aircraft weapons - a large-caliber machine gun, which was not effective against low-flying jets, but after the appearance of combat helicopters, from 1972 city, T-62 tanks began to be equipped with the DShKM anti-aircraft machine gun. For this, the shape of the tower in the area of the loader's hatch and above it was slightly changed. (on the same turret, as well as on the T-55) machine gun installed.
 commander's cupola. In the foreground — IR searchlight OU-3GK; under him — commander observation device TKN-3
commander's cupola. In the foreground — IR searchlight OU-3GK; under him — commander observation device TKN-3
Engine and transmission
The V-shaped 12-cylinder liquid-cooled diesel engine V-55V is used as a power plant on the T-62 tank, developing power 580 l. from. at 2000 rpm, same, as well as on the T-55. He also borrowed a power train with a hydropneumatic servo drive for controlling the main clutch. The gearbox has five speeds forward and one reverse. The roof of the MTO is similar to the roof of the T-55.
The booked volume contains fuel tanks with a capacity 675 l. Three additional fuel tanks were installed on the right fender and had a total capacity 285 l. The fuel reserve of the tank was up to 450 km (on the highway).
Speed characteristics and cross-country ability remained at the T level- 55: maximum highway speed 50 km / h, obstacles to overcome: rise up to 32 °, vertical wall up to 0,8 m, wide moat 2,85 m.
Production
Serial production of the T-62 in the USSR was completed in 1972 g. In Czechoslovakia, which received a license to manufacture T-62, they lasted longer on the assembly line - until 1978 g. Here the T-62 was produced at the 2TB plant. (Zavod Trucanske Stojarnе) in Martin, Slovakia, where it was then replaced by the T-72.
Tanks T-62, under construction in Czechoslovakia, were intended mainly for export to third countries. The Soviet Union satisfied its needs for these tanks on its own, and the T-62 was adopted by the Warsaw Pact countries only in Bulgaria. Information available, that North Korea also received a license to build the T-62, but the production of the T-62 in this country is unknown.
/Sergei Shumilin, naukatehnika.com/











