The breakdown of the finances of key European states and their dependence on the United States made the Entente allies at the Washington Conference dependent on the Americans. One of the reports from those years shows the amount of debt 64 states of the globe in 1913 and 1921 years. Changes in this matter, happened during this period, expressed in the following figures (at 1000 pounds):
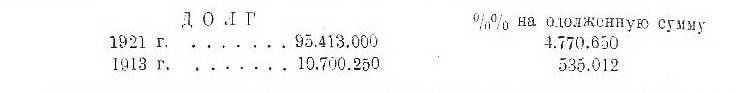
Table no 1
From these data we see, that interest alone reaches annually 44,6% total debt 1913 of the year. Thanks to such colossal financial burden, which increased the debt every day, debtors could not get out of the increasingly deepening financial crisis. Of the $95 billion in debt, Europe accounted for 88% debt. The remaining small portion of the world's debt fell on the United States., Asia, Australia, Africa and some European colonies. European debt is distributed as follows: share of countries in the anti-German coalition (England, France, Italy, Belgium, Romania. Yugoslavia, Poland) — 46575,50 million. pounds erased., share of the countries of the German coalition (Germany, Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Bulgaria, Turkey) — 30552,60 million. pounds erased., Russia's share - 5693,50 million., and only 1145,75 million. pounds erased. falls on the share of neutral European countries. In this way, over 98% European debt was owed to war-torn countries - which were unable to even pay interest.

London bank interior, 1920-is Mr.
The financial situation in Europe was constantly deteriorating due to the fact that, that the constant increase in paper issue was many times greater than the gold reserve, which in key European countries remained unchanged or gradually decreased, emigrating to the USA - which increased their gold reserves from 1887 million. dollars at the beginning of the war 3288 million. by August 1921 city, which was over 41% of all the world's gold cash.
Europe experienced colossal inflation (increase in the amount of paper money in circulation). I see, in particular, from the cited Manch Guardian Commerts from 22. 09. 1922 g. data on the number of people applying by August 1921 g. paper money (in million. corresponding monetary units):
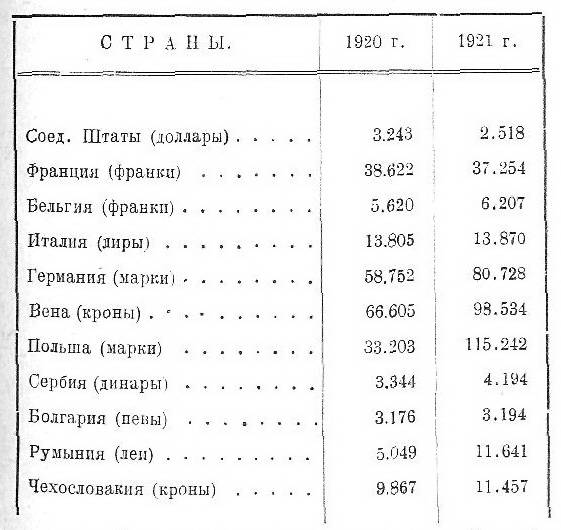
Table no 2
We see, what, Despite this, expenditure budgets for weapons were not reduced, as can be seen from the certificate of maritime budgets for 1920/21 and 1921/22 gg.:
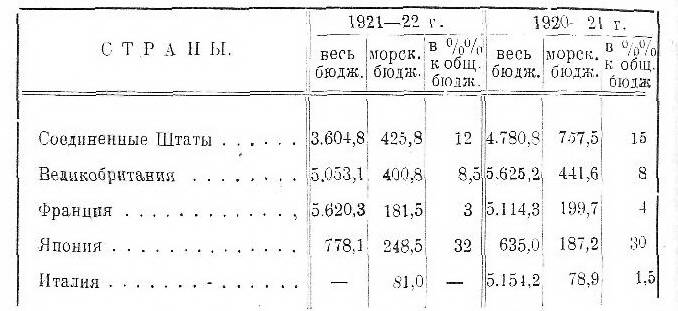
Table no 3
We see, that in this regard only the United States has made sensitive adjustments, while England, as a percentage of the entire budget, increased its maritime budget, and Japan increased it absolutely.
Monetary units lost (so far only when quoted on stock exchanges) their actual independence - and began to be measured in dollars. The dollar has become the absolute measure of stock trading. In the following table we show the fluctuations of the currency curve of the main units against the dollar (League of Nations statistical bulletin data). Having accepted 1913 g. for 100, we get the following for 1919 and 1920 gg. and monthly for 1921 of the year:
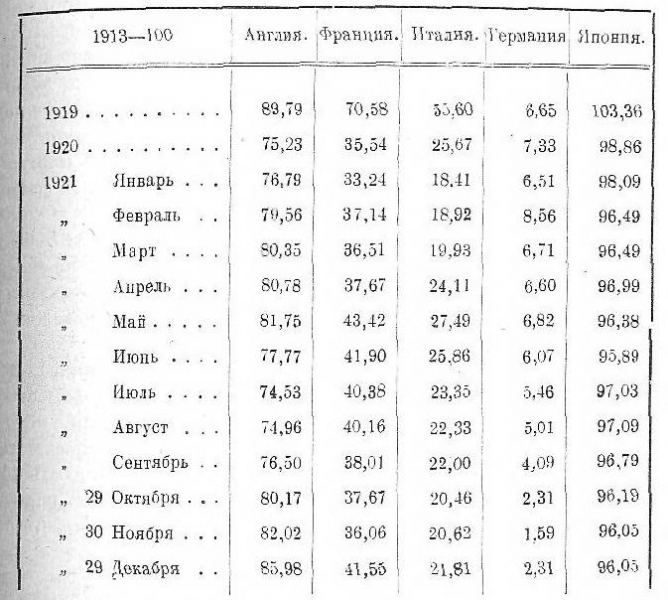
Table no 4
The numbers in this table speak for themselves. Two main conclusions can be drawn from them. At first, that the currency of the most financially stable states, like Japan, on the threshold 1922 g. costs less than a dollar. Secondly, Over the course of three years of economic “restoration”, the most powerful states not only failed to raise the exchange rate of their currencies, but their currency continued to depreciate, reaching for some of them (for example Germany) to a catastrophically low level. T. about., by the time of the Washington Conference, Europe found itself in an absolutely much more difficult situation, than three years earlier in Versailles.
To conclude our note with regard to the financial situation of Europe before the Washington Conference, data should also be provided, indicating Europe's direct financial dependence on the USA. In fact, there was no country left in Europe, not indebted to the United States. Data from the Economist magazine tell us this. 12 November 1921 g. with a list of debtors by June 1921 g. and indicating the amount of their debt (at 1000 dollars):

Table no 5
To this should be added the accrued, but unpaid interest amounting to a billion dollars - and 94% falls on the share of the victorious states - England, France, Italy and Belgium. The American financial “Octopus” has tightened its tentacles around the throat of an already war-stricken Europe. And if for 200 previous years to 1914 g. The British placed four billion pounds sterling in various countries of the world, then the Americans have placed fifteen billion abroad in one form or another over the previous six years alone.
No wonder, therefore, that in such conditions England did not seek to take a belligerent pose at the Washington Conference - the former Lady of the Seas became a supporter of limiting naval armaments.
Here's what the liberal British press wrote about this: "An atmosphere of warm and noble enthusiasm, which characterized the first days of the conference, replaced by a mood of bargaining. If we don't think about the final destruction of the war, if we intend to use our super-dreadnoughts in the future at least as a moral argument, which we keep in stock, then we are fools, that we are tying our own hands with some kind of agreement. If we really assume, that future conflicts will be resolved somehow differently, just not war, then why should we think, more or less our fleet, than American or Japanese! For offensive warfare across the Atlantic or in the Pacific, our naval forces are in any case insufficient; For defensive purposes, we don’t need to compete with our rivals at all.”.
Except for debtors of the first order (Debtors of America), During the First World War, debtors of the second order were formed. England, being a debtor to America, at the same time it is a creditor in relation to France and Italy: England owes it first 2700 million. dollars, and the second - 2312 million. dollars. Then come third-order debtors - small states, formed as a result of the war and financed by France.
This is, in general terms, the chain of financial interdependence in Europe, and also between Europe and America on the eve of the Washington Conference.
Oleynikov Alexey











