 A-20G bomber with radar "gneiss-2".
A-20G bomber with radar "gneiss-2".
In the Soviet Union, "Gneiss-2" radar went into serial production in the years of the Great Patriotic War, it happened in 1942 year. This aircraft radar mounted on the following models of planes: Double dive bomber Pe-2, heavy twin-engine fighter Pe-3, as well as the bomber Douglas A-20, who supplied the Soviet Union from the United States under the Lend-Lease Program. There were in the Soviet Union gathered more 230 stations of this type.
AT 1932 year of the Military and Technical Department of the Red Army in the Main Artillery Administration (GAU) People's Commissariat of Defense were transferred orders for the development of aircraft detection means. SAU with the consent of the Main Department of Industry elektroslabotochnoy instructed the Central Radio Laboratory in Leningrad to organize experiments to test the possibility of using reflected radio waves to detect air targets. The contract between them was signed in 1933 year, and already 3 January 1934 In practice, the detection of the aircraft with the help of the station was carried out, who worked in CW mode. Although the aircraft was able to detect at a distance of 600-700 m, the fact of detection was a success and has contributed to solving the problem future defense. conducted in 1934 year experiment is considered to be the birthday of the national radar.
TO 1939 year at the Leningrad Physico-Technical Institute (LFTI) scientific and experimental base has been created, which was engaged in radio waves. At the same time under the direction of Yu. B. Kobzarev (future academic) mock-up was created by the impulse radar "redoubt", in the future, the first production Soviet radar. The establishment of this radar station was a significant step forward, as it allows not only to detect air targets at long range, and almost all the possible heights, but also to continuously determine the azimuth, the speed of the objectives and mission of the range. Furthermore, Circular synchronous rotation of the two antennas of the stations it can detect a single aircraft and aircraft group, is in the air at different distances and different azimuths within its coverage area, carrying out surveillance of their movements at intervals of time (one turn antenna).
Thanks to several such radar, which were adopted under the designation "EN-2" (radioulavlivatel aircraft), Air Defense Command could to observe the dynamics of the air situation in the zone of a radius of up to 150 kilometers (range accuracy 1,5 km), timely identifying the enemy forces in the air and predicting their intentions. For scientific and technical contributions to the development of the first national early warning radar, which was launched into production in 1941 year, YU. B. Kobzarev, P. A. Pogorelko and H. I. Tchernetsoff Stalin Prize was awarded to 1941 of the year.
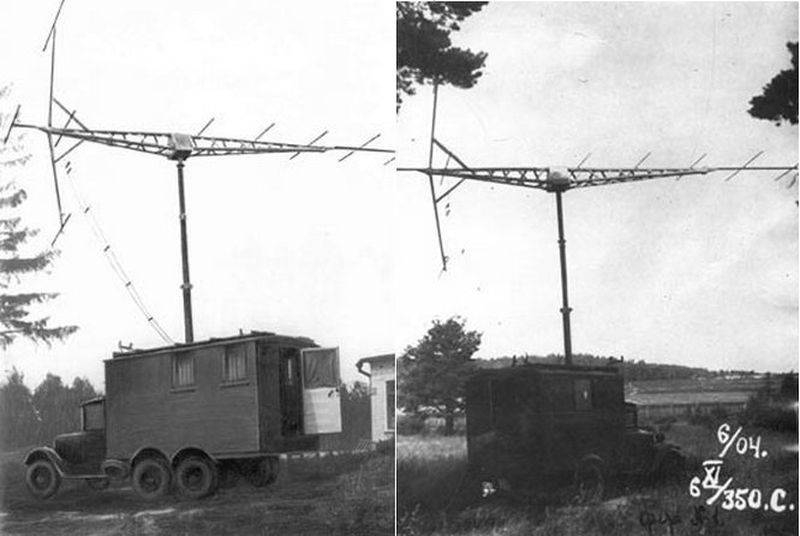 Radar early warning "RUS-2"
Radar early warning "RUS-2"
It is only natural, that along with the creation of the first stationary radar long-range, in the USSR and were working to create a radar, which could be installed on warships and aircraft. The development of the first Soviet aircraft radar, the designation "Gneiss-2", It was carried out already in the evacuation. Work on the creation of on-board radar led by Viktor Tikhomirov, who came to work in NII-20 (today it is the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Radio Engineering) at 1939 year. Graduated with honors from the Institute, he quickly joined the team of the defense company and was involved in work on regulation and delivery of the first Soviet long-range radar, which was put into service under the designation "EN-2" 1940 year.
It is worth noting, that at the Research Institute of Radio estimates, which were carried out in 1940 year, created on the basis of technologies of their time aviation radar with cables and power supply I had to weigh no less than 500 kg. Placing such equipment on board existing Soviet single-seat fighter was not possible. Further work is required of such a radar continuous service (at the level of the development of radio in those years question of automating the process could not,), that would distract the pilot from the piloting process. The way out of this situation was the installation of aeronautical radars in the multiseater plane. Here Soviet engineers did not invent the wheel, to exactly the same decision was made earlier and their British counterparts. At the suggestion of a test pilot NII VVS C. P. Supruna as a carrier of the first Soviet radar could perform dive bomber Pe-2, serial production of which Soviet industry has moved at the end of 1940 of the year.
At the beginning 1941 at the Research Institute of Radio has been assembled by a model of the onboard radar, Station received the designation "Gneiss-1". The first domestic aviation radar, it is natural, was imperfect and unfinished. In addition, in conducting experiments and trials it has been consumed the entire stock of generator tubes, klystrons centimeter range, which constitutes the heart of the onboard radar, and to order the production of new lamps turned simply nowhere. The Great Patriotic War forced to evacuate to the east, many Soviet industrial enterprises, including electro- and radio. Among the evacuees was also klystron developer - NII-9. Experts and equipment of the Research Institute were scattered on different plants, and the institution itself virtually ceased to exist. Subjected to evacuation and Research Institute of Radio, a new place in Sverdlovsk had to re-restore the necessary test and laboratory facilities.
Evacuation of NII-20 in Barnaul started in July 1941 of the year. At the new place almost "from scratch" in very difficult conditions the first domestic aircraft radar was created using the catastrophic lack of necessary equipment and trained personnel under the direction of Tikhomirov, received the designation "Gneiss-2". Just a few months was able to complete the tests of prototypes station, which have been found to be successful, after which the first onboard radar off the front.
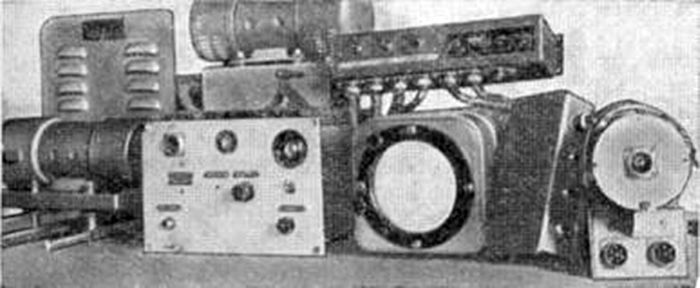 The payload onboard radar "Gneiss-2"
The payload onboard radar "Gneiss-2"
About, how rates were works on the creation of the first Soviet aircraft radar, can be judged from the following facts. equipment manufactured, without waiting for the release of documents. Installation of the radar carried on the concept of work and sketches of, already in the course of getting rid of the resulting defects and making changes. As a result, the effort first "flight" sample RLS "gneiss-2" was available at the end 1941 of the year. Power station radiation was 10 kW, she worked with a wavelength 1,5 m.
In January 1942 year at the airport, Located near Sverdlovsk, Radar "Gneiss-2" installed on the bomber Pe-2. Shortly thereafter began testing station. It is worth noting, that controls and indicator board radar "Gneiss-2" is located in the cockpit radar operator (this place was previously the navigator), and part radar units installed in the cockpit radio operator arrow. As a result of such changes in the aircraft turned double, slightly reduced the combat capabilities of the machine. In parallel with the evaluation of a new radar performance, which at that time was still experimental, was the process of working out the tactics and methods of combat employment of aircraft, equipped with radar. The primary role for this aircraft was a night fighter role.
to create a work station personally led in. AT. Tikhomirov, from the Air Force with the project worked E. FROM. Shtyein. When testing station as the target used Sa Soviet bomber. Debugging and debugging of radar equipment was carried out in non-stop operation, engineers worked directly at the airport. Occurred antenna verification process type, equipment failures eliminated, to change the design station.
During the work was able to reduce the "dead zone" to radar 300 m, and later to 100 m, as well as improve the reliability of its work. In this case, the team and the SRI-20 leadership understands the importance of creating a similar radar. Labor enthusiasm of the engineers and ordinary workers allowed in the difficult days of the war before the completion of ground tests, to release the first of a series of 15 Radar "Gneiss-2" for combat aircraft equipment Pe-2 and Pe-3. The first combat use of aircraft, equipped domestic radar, held at the end 1942 year near Moscow.
 Pe-2 with radar «Gneys-2»
Pe-2 with radar «Gneys-2»
In July 1942 the station "Gneiss-2" was able to successfully pass the state tests. The pace of development and commissioning of such a complex product in wartime has been impressive. In January 1942 , the first airborne radar mounted on the Pe-2, It begins the process of testing. Already at the end 1942 year planes, equipped with radar "Gneiss-2", take part in combat missions at Moscow, and then participate in the Battle of Stalingrad. 16 June 1943 the station was officially adopted by the Soviet Air Force. AT 1946 year for the development of the aviation radar "Gneiss-2" Tikhomirov received a second Stalin Prize.
In the course ended in July 1942 year state tests the following results were obtained:
- detection range of air targets such as a bomber - 3500 m;
- the accuracy of targeting the angular coordinates ± 5 degrees;
- the minimum flight altitude in the search of the enemy - 2000 m (minimum height, where the problem disappeared, associated with the reflection of radio waves from the Earth's surface).
At the end 1942 at the busiest time of the Battle of Stalingrad Tikhomirov, together with the development team left for the place of fighting. Here the engineers engaged in the installation and commissioning of radar on bombers Pe-2. Tikhomirov he often flew as an operator "Gneiss-2 'radar and was personally involved in instructing pilots. Tikhomirov equipped aircraft used by the Soviet command to block the "air bridge", that the Luftwaffe tried to provide for the supply of various goods encircled Stalingrad grouping Paulus. In this way, the first Soviet planes with radar contributed to the defeat of the Nazis on the Volga River. Routine tests with "Gneiss-2" radar Pe-2 aircraft took place already in 1943 year, they went near Leningrad.
In the period from February to May 1943 year planes, equipped with radar "Gneiss-2", used in the Leningrad Air Defense System. They were part of the 24 th Guards Fighter Aviation Regiment of the second body defense. When intercepting air targets night fighters were directed at the target by means of ground radar early warning RUS-2, and when approaching enemy planes using their onboard radar. Finding an aerial target, onboard radar operator "Gneiss-2" passed the necessary instructions to the pilot for closer relations with the aim of.
 A-20G bomber with radar "gneiss-2"
A-20G bomber with radar "gneiss-2"
AT 1943 was an improved version of the radar was set up in the USSR, were designated as "Gneiss-2M". At the station we used a new antenna, which can detect not only airborne targets, but the enemy surface ships. In the autumn 1943 year, this station was tested in the Caspian Sea, after which it was put into service and put into serial production. In total by the end of 1944 , it was created in NII-20 more 230 airborne radar "Gneiss-2".
From February to June 1943 years were tested radar "Gneiss-2" with the American bomber A-20, I considered the possibility of its use as a night fighter. Compared with bomber Pe-2 supplied by Lend-Lease The aircraft has a number of advantages, so in July 1943 year began the creation of the 56th Air Division long-range fighters. The division consisted of two regiments (45-he and 173 it), military aircraft A-20. Each regiment was put on staff have 32 aircraft and 39 crews, In addition, in the regiment was part of a radar company, which was equipped with radar early warning RUS-2.
Obey this division AFLRO (ADD). From May 1944 year shelf division arrived to the front and were used to ensure the safety of major transport hubs. In addition to the fight against enemy aircraft, aircraft, equipped with "Gneiss-2", also used in torpedo air regiments for the detection of surface ships of the enemy.
In addition to airborne radars "Gneiss-2" and "Gneiss-2M" own production, during the war in the Soviet aircraft were installed and American radars. Total US sent its allies more 54 thousands of airborne radars, mostly it was for the supply of UK. In the Soviet Union it was delivered 370 two types of radars: 320 - SCR-695 and 50 – SCR-718. After the completion of the Great Patriotic War - in the second half 1945 in the USSR was adopted by and put into serial production aircraft radar "Gneiss-5". As a result, the state tests demonstrated this radar detection range of air targets 7 kilometers (at the height of the target flight 8000 m).
Information sources:
— airwar.ru/enc/fww2/pe2gneys.html
— hist.rloc.ru/lobanov/3_01.htm
— Bartenev VG, Russia - the birthplace of radio. historical sketches.











