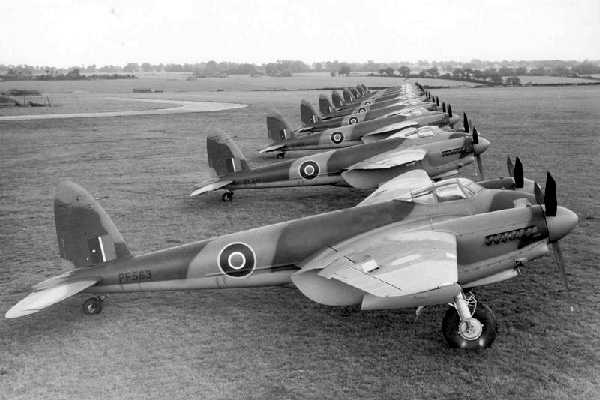
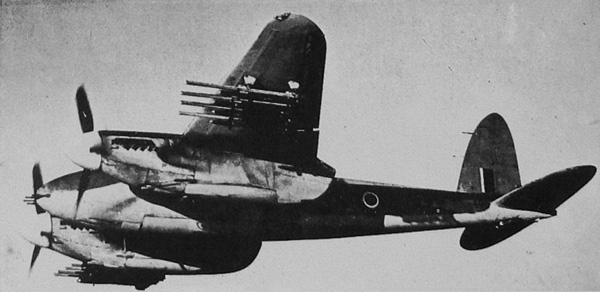
Solid wood double twin-engine combat aircraft, It existed in many guises – high-speed bomber, scout, fighter-bomber, night fighter. Development of machines under the brand designation DH.98 was conducted based on the experience, resulting in the construction of high-speed aircraft and passenger liner DH.88 DH.91. Initially developed as an aircraft speed bomber in accordance with specification R. 13/36.
Mosquito bomber – video
revolutionary concept, proposed designers "De Havilland", It provided a complete rejection of defensive weapons. Such an approach is long rejected by the Ministry of Aviation, and only at the end of December 1939 g. was an order for prototype construction, and soon – and the first installment in 50 aircraft. In July 1940 g. It was received instruction to build one of these aircraft in the fighter variant, and in October framed corresponding specification F. 18/40, It provides for the establishment on the basis of "Mosquito" night and escort fighter. fighter prototype testing began 15 May 1941 g. The fighter version of most of the first batch of aircraft was built, and then into production successively introduced a number of new modifications. In total, the British built 1824 night fighter and 2648 Fighter-bombers "Mosquito"; Besides, fighter-bombers were produced in Canada (343 Aircraft) and Australia (189 machines).

Service and combat use
Night fighters "Mosquito» NF Mk.II first began to develop at the turn 1941/1942 gg. 151-squadron, and in May – 264-I. The first sortie 157th AE made in late April, but only 29 May 1942 g. The first aerial victory was recorded. In February 1943 g. adopted 85 Squadron began arriving aircraft "Mosquito» NF Mk.HI much more efficient radar centimeter range). Such aircraft have been used successfully not only against the twin-engined bombers Do 217 (the first victory recorded in the night 14 on 15 April 1943 city), but also anti-single-FW 190A and the latest Me 410. Late autumn in parts appeared NF Mk.XIII and NF Mk.XVII, and in the early 1944 g. as part of Fighter Command to the "Mosquito" is already flying 10 night squadrons.
In November 1943 g. three squadrons of night fighters (141-Yu, 169-th and 239 th) handed Bomber Command, forming 100th group, and in May 1944 g. they were joined by the 85th and 157th AE. escorting bombers, they acted over enemy territory, engaging in combat with the newest German night fighters not 219, and later -even with reactive Me 262. The same squadron, that remained in the air defense system, shifted to the fight against flying bombs V-1. In total, by the end of the war on account of the night "Mosquito" was about 600 downed enemy planes and about the same V-1.

As a fighter-bomber was the first to apply the "Mosquito» F Mk.II 23rd AE. Her aircraft act as TN. "Intruder", striking airfields and trains on the territory of occupied France by the Nazis, Belgium, Netherlands. Since October 1943 g. over France acted FB Mk.VI «Mosquito". First they start to apply the 140th Wing (21-I, 464-I and I-487 AE). His aircraft during daylight hours struck by vehicles, objects of railway infrastructure, power plants, important industries. Since February 1944 g. such operations has joined 138th wing. In the same month, "Mosquito» FB Mk.VI appeared in Bomber Command – 515 Squadron 100th group. To summer 1944 g. This group had already 4 AE fighter-bombers "Mosquito". If the aircraft 138 th and 140 th of the wings on the eve of D-Day and after it acted on the objects near the bridgehead (bridge, Staff and others.), the FB Mk.VI 100th group struck at targets deep in enemy territory, Firstly, airfields. "Mosquito" were combat work almost until the end of the war in Europe, As a last sortie 4 May 1945 g.
After the war fighter modification "Mosquito" were delivered to Belgium (NF Mk.ZO), Sweden (NF Mk.XIX), Yugoslavia (FB Mk.VI and NF Mk.38), France (FB Mk.VI and NF Mk.ZO), Czechoslovakia (FB Mk.VI), Turkey (FB Mk.VI), Dominican Republic (FB Mk.VI), Israel (FB Mk.VI), homyndanovskomu China (FB Mk.26).
Ideology, planted J.. De Havilland to create "Mosquito", It confirmed its correctness. Aircraft, conceived as a bomber, It has been successfully transformed into a night fighter (becoming the best British aircraft in this class) and fighter-bomber. Exceptional performance characteristics become a kind of benchmark, for British designers, for the enemy – the task of countering "Mosquito" was one of the determining factors in the formation of the Luftwaffe fighter image.
modifications Mosquito
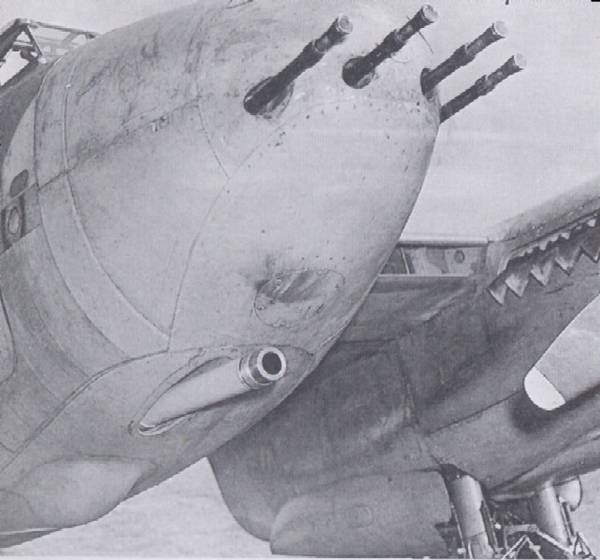
«Москито» F Mk.II – engines «Merlin» 21, 22 or 23 (1480 hp). weaponry – 4 20-mm cannon at the bottom of the fuselage, 4 7,7-mm machine guns in the bow. released 494 Aircraft, most – in night embodiment NF Mk.II with radar or AI Mk.IV Mk.V. 25 aircraft converted into a version of NF Mk.ll(Special) radar and dismantled with increased fuel.
«Москито» NF Mk.XII – РЛС AI Mk.VIII, no guns. Pereoborudovano 98 aircraft of NF Mk.II.
«Москито» NF Mk.XIII – engines «Merlin» 21, 23 or 25 (1610 hp), weapons and radar – as the NF Mk.HI. Under the wing provides for the suspension of the PTB. Since August 1943 g. constructed 260 copies.
«Москито» NF Mk.XV – high-altitude version with pressurized cabin, two-stage turbochargers on engines, increased wingspan. Pereoborudovano 5 aircraft of NF Mk.ll.
«Москито» NF Mk.XVII – RLS AI Mk.H (American SCR-720), weaponry – like NF Mk.XII. Pereoborudovano 99 aircraft of NF Mk.II.
«Москито» NF Mk.XIX – engines «Merlin» 25. Apply universal nose cone, allows you to set the radar AI Mk.VIII or Mk.H. From April 1944 g. to September 1945 g. released 280 copies.
«Mosquito» NF Mk.30 – high-altitude version of the NF Mk.XIX with engines "Merlin" 72 or 76 (1685 hp) with two-stage turbocharger and radar AI Mk.X. Since June 1944 g. constructed 526 aircraft.
"Moskito" NF Mk.36 – postwar version with motors "Merlin" 113/114 (1640 hp) or 113A / 114A and radar radar AI Mk.H. Since June 1945 g. fabricated 163 fighter.
"Moskito" NF Mk.38 – engines «Merlin» 114A, РЛС AI Mk.IX. constructed 101 a car.
«Mosquito» FB Mk.VI – fighter-bomber. Engines «Merlin» 21, 22, 23 or 25. weaponry – 4 20-mm cannon, 4 7,7-mm machine gun; possible suspension 2 113-kg bombs in the bomb bay and 2 under the wing (instead of the last – to 8 THEIR). Since February 1943 g. fabricated 2584 instance. In this way, This modification has become the most massive of all the "Mosquito".
«Москито» FB Mk.XVIII – antiship variant, armed 57mm cannon (ammunition 18 shells) and 4 7,7-mm machine guns. Pereoborudovano 19 aircraft from FB Mk.VI.
«Mosquito» FB Mk.21, FB Mk.24 и FB Mk.26 – FB Mk.VI Canadian counterparts. FB Mk.21 (3 Aircraft) engines had "Merlin" 31, FB Mk.24 (2) – "Merlin" 301, a FB Mk.26 (338 units, issued in February and August 1945 city) – "Pakkard-Merlin" 225 (1620 hp)
"Moskito" FB and FB Mk.40 Mk.41 – FB Mk.VI Australian counterparts with engines "Merlin" 31 (1460 hp). constructed 178 Mk.40 and FB 11 FB Mk.41.
"Sea Mosquito" Mk.ZZ TF and TF Mk.37 -poslevoennye carrier-based fighter-bomber with engines "Merlin" 25, reinforced chassis and folding wings. weaponry – like FB Mk.VI (except for machine guns). Mounted radar ASH (TF Mk.ZZ) или ASV Mk.XIII (TF Mk.37). manufactured 50 TF and Mk.ZZ 14 TF Mk.37.

Performance characteristics Mosquito B Mk.I
– chief designer: Ronald Bishop
– First flight: 25 November 1940 of the year
– End of operation: 1953 (The royal Air Force)
– years of production: 1940—1950
– units produced: 7 781
Mosquito crew
– 2 man
Dimensions Mosquito
– Length: 12,43 m
– Wingspan: 16,51 m
– Height: 4,65 m
– wing area: 42,18 m²
weight Mosquito
– empty weight: 6 490 kg (14 300 pounds)
– Curb weight: 8 210 kg (18 100 pounds)
– Normal takeoff weight: 9 900 kg
– Maximum takeoff weight: 11 000 kg (25 000 pounds)
engine Mosquito
– Power point: 2 × Rolls-Royce Merlin 21
– engine power: 2 × 1 480 HP (2 × 1 100 kW)
Mosquito speed
– full speed: 668 kmh
– Cruising speed: 491 kmh
– combat radius: 2655 km
– Skoropodъёmnost: 14,5 m / s
Practical ceiling Mosquito
– 11 000 m
armament Mosquito
Small-pushechnoe:
– 4 × .79″ (20 mm) Hispano Mk II (fuselage)
– 4 × .303″ (7,7 mm) pulemёtы Browning (nasal)
bombs: to 908 kg (1 × 454 kg + 2 × 227 kg or 4 × 227 kg)
Photo Mosquito