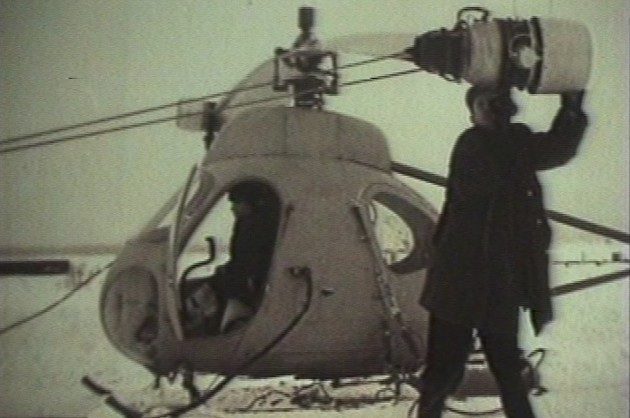
In the mid-50s, when designing the helicopter Mi-6 was basically completed, EDO Mil designers began to search for promising ways to further increase load capacity rotorcraft. One of the priorities in those years was considered the creation of a jet-powered helicopter rotor, ie. with drive, wherein the torque screw force generated reaction gases.
Helicopter B-7 – video
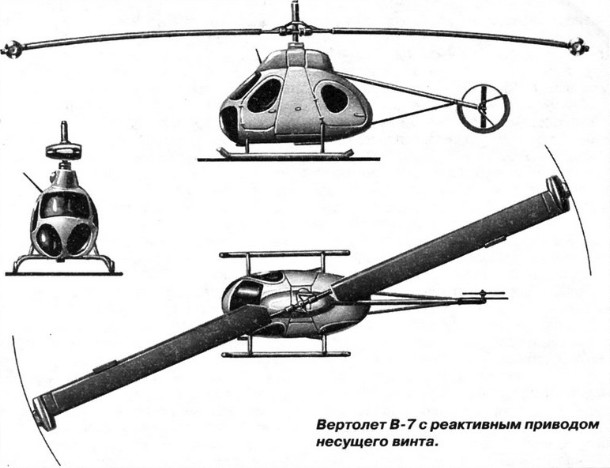
Gases derived from established at the ends of the blades of jet engines, or jet nozzles. Refusal of a manual transmission was not only to simplify and facilitate the design of the helicopter, but also significantly affect its weight perfection. Besides, thus absent the reactive torque of the rotor, and consequently, there was no need for energy-intensive and cumbersome means of his parry, which also simplifies the layout of the helicopter. Of all types of Jet drives seemed the most economical drive by TRD. The bureau is developing a project of such a super-heavy-lift helicopter (In one of the projects 16) a rotor diameter of about 60 m. At the end of each blade was assumed to install two turbojet engines with counter-rotating turbines and a thrust of 1750kg each. But previously M. L. Miles was going to build a small experimental four helicopter, which was to test the jet drive the rotor and to solve specific problems such scheme. He managed to interest his idea first representatives of CAF, and then the military, and 20 December 1956. the government issued a decree on the development of a helicopter pilot in the 7-jet driven rotor.

Design and construction of rotorcraft, the smallest and lightest ever built Mil OKB, We moved very quickly. In December 1957,. detailed design was largely completed, and pilot production plant №329 laid right series of five machines. The lead designer of B-7 was appointed A.V.Kochkin, and then - G.G.Lazarev.
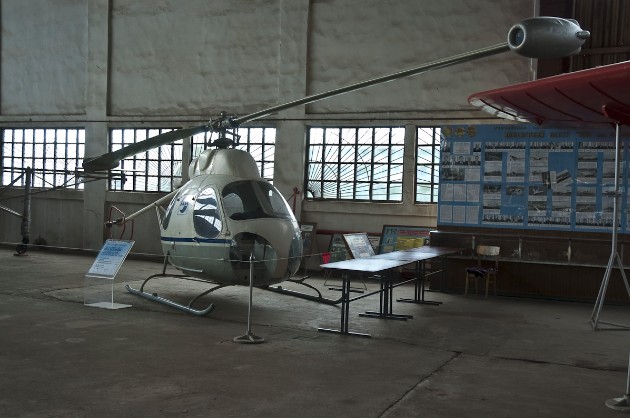
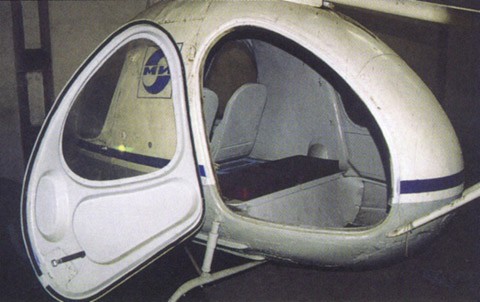
helicopter design was as simple as possible. The basis was the teardrop-metal semi-monocoque fuselage riveted construction. In the upper part of load-bearing frames mounted on the bolt cast slab. To the plate was mounted gearbox flange, consisting of the rotor shaft and the drive units. On the rotor shaft sleeve with installed blades and the swash. To the front end plate joined bracket with rocking chairs and steering control. On each side of the fuselage were three doors. The cabin, in addition to the pilot, can accommodate three passengers or a stretcher with the patient and accompanying medical staff. The fuel tank is located under the floor. Directing the fuel pump to the fuel controller, from which it received in the rotor shaft collector and from there under the influence of centrifugal force - to the TRD, located at the ends of a two-blade rotor.

The blades were rectangular steel spar, wooden frame and plywood sheathing. They were attached to the sleeve by means of axial and overall horizontal hinges. two tubes were laid into socks ribs blade fuel supply. Wiring held inside the spar. On top of the end of the rotor shaft mounted collector devices powerplant. In the development of directional control system, first planned to limit tail, established in an inductive flow, but accompanied by the development of B-7-depth investigation of models in a wind tunnel have shown the need to keep the tail rotor. It was established back of the fuselage on the short tubular farm. In this way, avoid installing the transmission to the helicopter failed. B-7 Mil OKB designers for the first time applied the skid landing gear.
Mounted on served to prevent ground resonance hydraulic shock absorbers rear transverse tubes. The helicopter was equipped with a 7-lightweight set a flight instrumentation, provided for by its military option with weapon system.
Successful implementation of the idea of the helicopter jet driven rotor depended primarily on the creation of a sufficiently light and small engines, able to operate reliably in the field of centrifugal forces at high accelerations, as well as fuel supply and control systems of. Of the many heads of Aircraft Engine Design Bureau, involved in this task, for the design of special TRD took only chief designer AGIvchenko. Developed in its DB-478 motor thrust AI-7 70kgs is a simple turbojet engine with a centrifugal compressor and a single stage turbine. For the purpose of balancing the gyroscopic moments engine was configured with three flywheels, rotates in the direction of, opposite turbine. The decision was simple, but, as subsequent events showed, wrong.
AI-7 were obtained by the motors №329 only in December 1959, helicopter itself was assembled long before. Immediately after the first run had problems TRD: the engine is not out on the operating speed, and did not develop a given traction because of the large selection of power on the handwheel. Therefore, they had to be removed from the engine. For cooling oil system overheats Mil OKB engineers designed a unique tubular oil cooler, placed around the engine air intake. Now AI-7 developed predetermined cravings, but the load of the gyroscopic moment began to perceive support system.

The implementation of the concept of a helicopter jet driven rotor was much more difficult, than expected. Lapping B-7 and its powerplant dragged. In order to improve the AI-7 CIAM specialists were involved. It took a few years to solve problems of maintenance of engines in the field of centrifugal forces, but only 19 February 1962. the first attempt was made to rise into the air B-7 on a leash. But the helicopter could not get off the ground. Under the influence of gyro moment engine rotor blade at a negative angle swirled, it covers the corrugations of the blades, which created a lot of resistance to rotation, Reinforced nezakapotirovannymi engines. Besides, power steering collective pitch was insufficient to overcome the control system loads. Vibration of the helicopter were large. After this test, the engines were sent to the alteration in the bureau AGIvchenko, blades repaired, hydraulic control system common step was replaced by a more powerful, for engines designed hoods.
Salon helicopter B-7
In April 1965,. Test B-7 on a leash resumed, but when first run has jammed one of the engines. I had to return it back to the manufacturer. Finally 20 September twice managed to achieve stable hovering. Tests conducted mechanic V.A.Kolosov. Hanging occurred with decreasing rotor speed, since in this case the motor produce less torque and blades are not twisted or warped. According to the program, 1965. planned evaluation of the actual power at various operating speeds of the rotor, however, this year was the last in the history of the development of B-7. 11 November 1965. during the tests at the maximum speed of the main rotor and engine takeoff mode occurred almost simultaneous destruction of both engines. As it turned out, take-off mode of the engine AI-7 was a critical. engine turbochargers entered the resonant vibrations and, broke down the body, "Flown" together with the rear of the engine. The helicopter is smoothly without damage down to earth.
The cabin of the helicopter B-7

The designers were forced to admit the further operational development of AI-7 futile. They are pinning their hopes on the CIAM developed a new turbojet MD-3, gyroscopic moment at which counterbalanced due to opposite rotation of the turbine and the compressor. But this engine needs a long fine-tuning, as, however, and many other elements of the helicopter. Fuel consumption at the circuit with jet-driven rotor was much longer, than originally anticipated. It was high, and the noise level. Then Mil concludes, that increase the helicopter payload more favorably by using mnogovintovyh circuits with mechanical transmission. Lapping B-7 was discontinued.

AI-7 helicopter B-7
The performance characteristics of the helicopter B-7
– First flight: 1962 year
B-7 crew
– 1 human
Capacity-7
– 3 passenger
Dimensions B-7
– Length: 6,23 m
– The diameter of the rotor: 11,60 m
– Height: 2,91 m
Weight-7
– empty weight: 730 kg
– Normal takeoff weight: 835 kg
– Maximum takeoff weight: 1050 kg
Engines B-7
– Make engine: 2 × various AI-7
The 7-speed
– full speed: 240 kmh
– Cruising speed: 210 kmh
Flight range B-7
– 510 km (practical), 1000 km (Ferry)
Practical ceiling-7
– 4500 m











